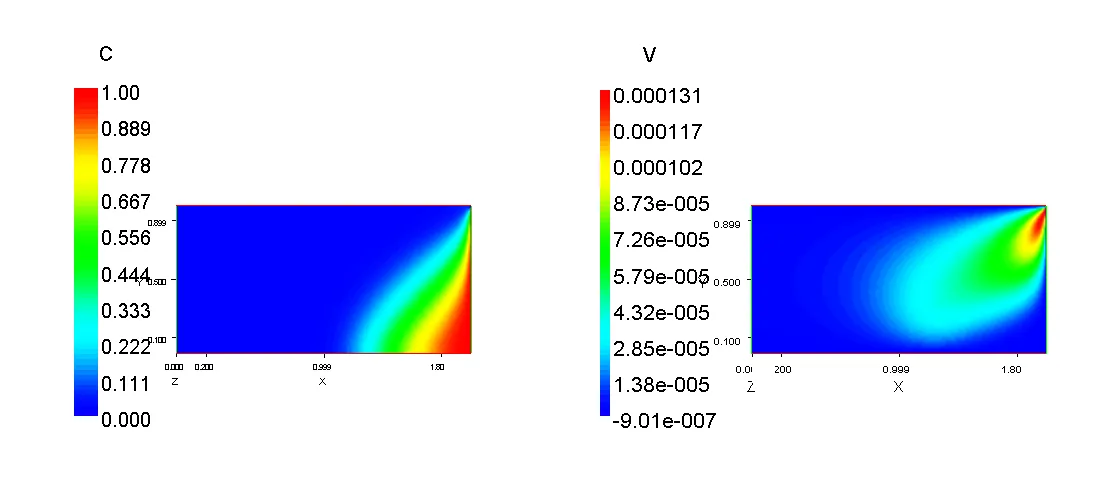
Saline intrusion commonly affects coastal aquifers, forming a Ghyben-Herzberg Lens where saltwater penetrates underneath the freshwater layer as freshwater recharge decreases. This intrusion can disrupt agricultural activities and contaminate water supplies.
Objective: The study aimed to examine the relationship between recharge rates (from sources like rivers and rainfall), pumping activities, and coastal conditions to understand and mitigate saline intrusion.
Solution: PORFLOW® was used to simulate flow fields and saline lens location in a widely accepted “standard” validation scenario.
Outcome: The study demonstrated how PORFLOW® can effectively model saline intrusion dynamics, providing valuable insights for managing coastal water resources and protecting agricultural and potable water supplies.